Snapdragon X75 5G achieves a 7.5 Gbps downlink speed
Unveiled during MWC 2023, the Snapdragon X75 5G network data chip was recently announced by Qualcomm to achieve peak downstream transmission speeds of up to 7.5 Gbps in the sub-6GHz frequency range, in a standalone network environment with 4-carrier aggregation TDD connection mode, combined with 1024 QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation).

The Snapdragon X75 5G network data chip complies with the 3GPP-defined Release 18 specification, primarily incorporating 5G advanced application features. It not only integrates connection capabilities in the sub-6GHz and millimeter wave frequency bands but also combines with the Snapdragon satellite connectivity feature unveiled earlier at CES 2023.
Furthermore, the Snapdragon X75 5G chip synergizes with Qualcomm’s second-generation 5G Artificial Intelligence processor, optimizing 5G network transmission through AI technology, and minimizing power consumption to extend device battery life.
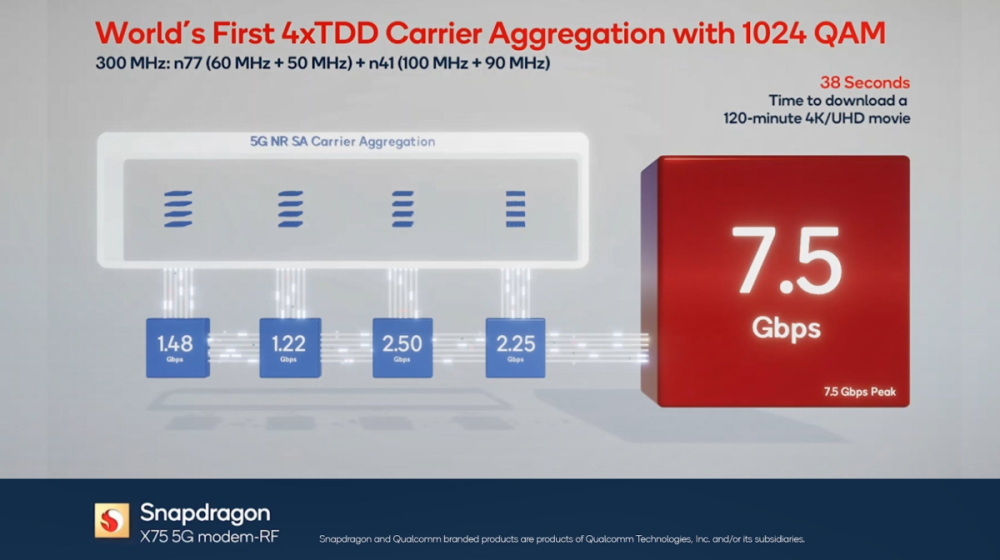
In achieving this transmission speed of up to 7.5 Gbps in the sub-6GHz frequency range, it utilizes the n77 frequency bands of 60MHz and 50MHz, along with the n41 bands of 100MHz and 90MHz, resulting in a total bandwidth of 300MHz. This allows for the completion of download transmission tasks for 4K UHD quality movie content, lasting 120 minutes, in just 38 seconds.
Beyond its application in smartphones, Qualcomm also highlighted the broad applicability of the Snapdragon X75 5G network data chip in domains such as intelligent vehicular technology, mobile communication, computer computation, industrial Internet of Things, public or private network construction, and more. It further includes corresponding satellite connectivity application modes, thereby satisfying a more diverse array of network connection needs.
Qualcomm is currently providing clients with testing units of the Snapdragon X75 5G network data chip, with the expectation that it will be implemented in commercially available products in the latter half of this year. These will include individual connectivity devices or mobile products, likely also to be utilized in the forthcoming flagship-level Snapdragon processor set to be announced later this year (presumably the Snapdragon 8 Gen 3).




