Intel is advancing the goal of 5 process nodes within 4 years
At the Intel Technology Tour 2023 MTL Tech Day event, Intel underscored its sustained focus within the Client Computing Group (CCG) on the realms of creation, connection, gaming, as well as professional and educational applications. They emphasized their previously announced ambition to advance through five process nodes within four years. To date, they have successfully launched two of these nodes: Intel 7 and Intel 4. The transition to the Intel 3 process is anticipated for the latter half of this year, with plans to usher in the Intel 20A process in the first half of 2024, and subsequently, the Intel 18A process in the latter half of the same year.

In light of competitors such as TSMC and Samsung already venturing into the 3nm process development, Intel, which historically grappled with procedural technological stagnation, is fervently striving to recover ground lost in this sector by realizing its goal of five process nodes within a four-year span.

In 2022, Intel adeptly progressed its manufacturing process to the Intel 4, roughly equivalent to TSMC’s 7nm to 5nm processes. The imminent Intel 3 process is posited to be commensurate with TSMC’s 5nm to 3nm, while the Intel 20A and 18A processes are expected to parallel TSMC’s 3nm to 2nm and 2nm to 1.4nm processes respectively.
Presently, Intel’s 3, 20A, and 18A processes are all poised for preliminary mass production. Intel aspires for the 18A to seamlessly transition to full-scale production by 2025, intended for their next-gen processor codenamed ‘Lunar Lake’, which will integrate VPU artificial intelligence components among other designs. Additionally, collaboration with Arm has been confirmed to manufacture a new architecture processor using the Intel 18A process.
For forthcoming processor designs, Intel conveyed its intent to cater to the burgeoning demand for AI computation in the market. This involves the extensive integration of AI computation accelerators, bolstering graphical computing prowess, thus promoting efficient AI computations, all while significantly enhancing performance per watt, satisfying intricate AI computation demands.

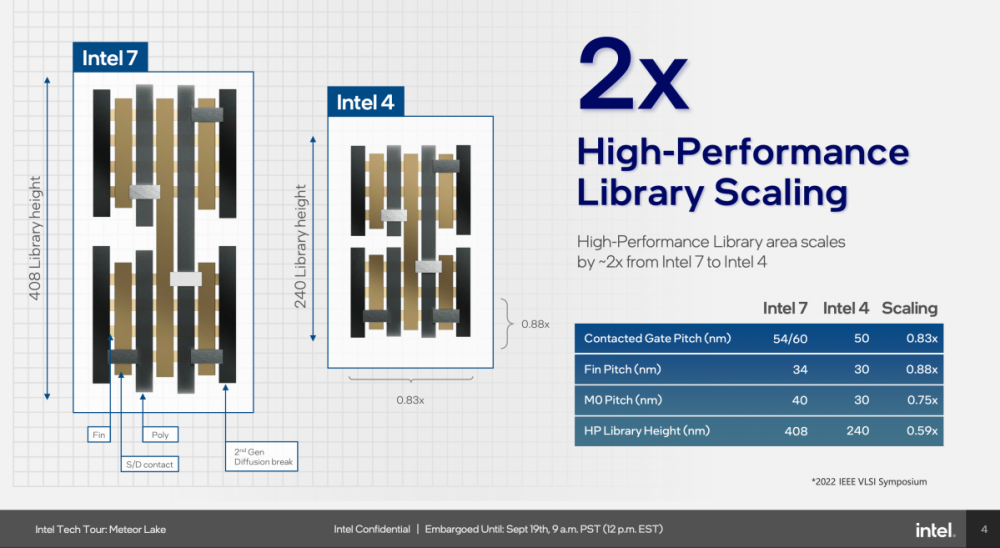
Regarding the Intel 4 process employed by their 14th generation Core processor, codenamed Meteor Lake, Intel elucidated that it will double the transistor density for high-efficiency computing compared to Intel 7. Employing extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUV) technology facilitates a more refined manufacturing design, and when juxtaposed with the Intel 7 process, offers a performance boost of over 20% in power efficiency.
The incorporation of EUV technology simplifies the manufacturing workflow, favoring mass production. It ensures an uptick in production yield and augments the power efficiency of the processor designs, striking a balance between computational performance and energy efficacy.

Intel further accentuated its proprietary EMIB packaging and Foveros stacking technologies, enabling processors to accommodate a greater number of transistors, computational components, and I/O controllers within a more compact area. Notably, the 14th generation Core processor, codenamed Meteor Lake, will adopt the novel Flexible Tiled architecture, amalgamating the majority of key components through Foveros Advanced stacking technology, facilitating a more compact processor capable of driving heightened computational performance at a reduced power footprint.






