Threat Alert: TA547 Targets Germany with Rhadamanthys Stealer
In March 2024, cybercriminals launched an attack on dozens of organizations in Germany using a PowerShell script, presumably developed with the aid of artificial intelligence. The campaign involved the distribution of the infostealer Rhadamanthys.
Experts at Proofpoint attributed the campaign to the group TA547 (Scully Spider), an Initial Access Broker (IAB) that has been active since 2017. This group specializes in disseminating various types of malware for Windows and Android systems under a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) model.
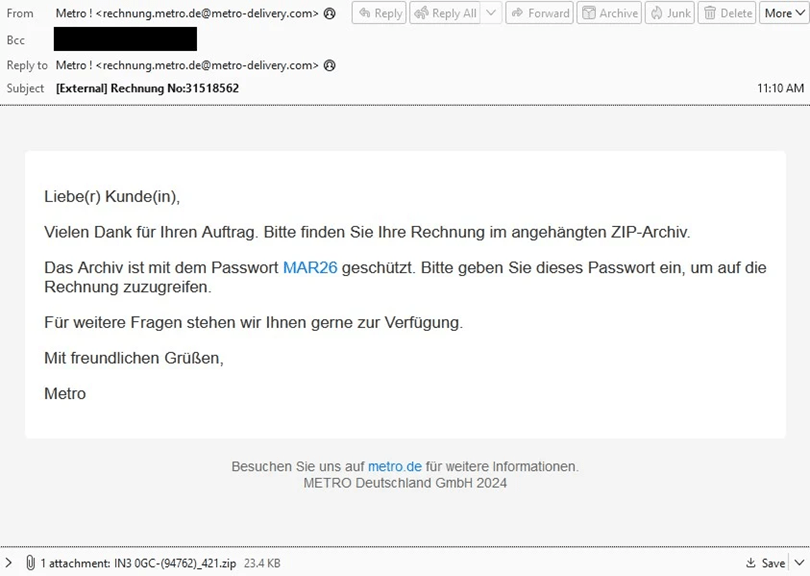
Example TA547 email impersonating the German retail company Metro.
Recently, TA547 has begun utilizing Rhadamanthys, a modular information-stealing system that continuously expands its data collection capabilities, including clipboard data, browser data, and cookies. During this campaign, TA547 disguised itself as the well-known German brand Metro, using invoices as lures, which were distributed via email.
Rhadamanthys was spread through password-protected ZIP archives containing a malicious LNK shortcut. This shortcut triggered the execution of a PowerShell script, which in turn launched Rhadamanthys, encoded in Base64. Researchers explain that this method allows the malicious code to execute in memory, avoiding any disk interaction.
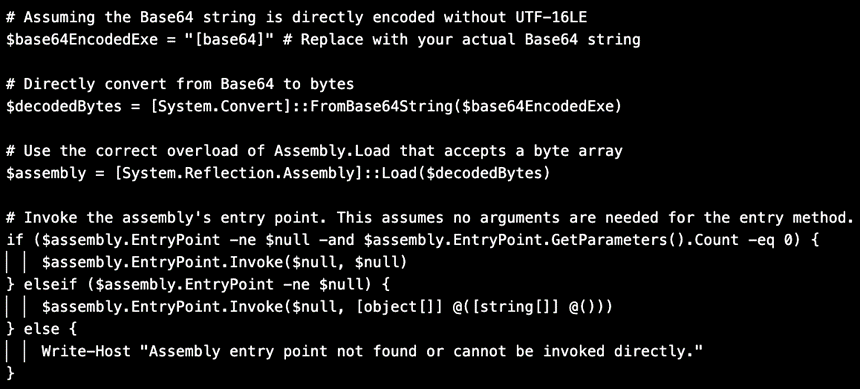
Example of PowerShell suspected to be written by an LLM and used in a TA547 attack chain.
Notably, the PowerShell script exhibits unique characteristics typical of AI-generated code (ChatGPT, Gemini, or Copilot), such as impeccably grammatical comments and a specific structure and naming of variables, suggesting the use of generative AI in creating or modifying the script.
Proofpoint emphasized that AI-generated code is distinguished by high-quality comments, which are unusual for human-generated code. Experiments have shown that results obtained with systems like ChatGPT are similar to the analyzed script, further supporting the theory of AI utilization.





