Service control and runlevel in Linux
How to control the running status of the service?
Service Control
ntsysv
ntsysv is a simple interface for configuring runlevel services which are also configurable through chkconfig. To start the utility, type ntsysv at a shell prompt as root.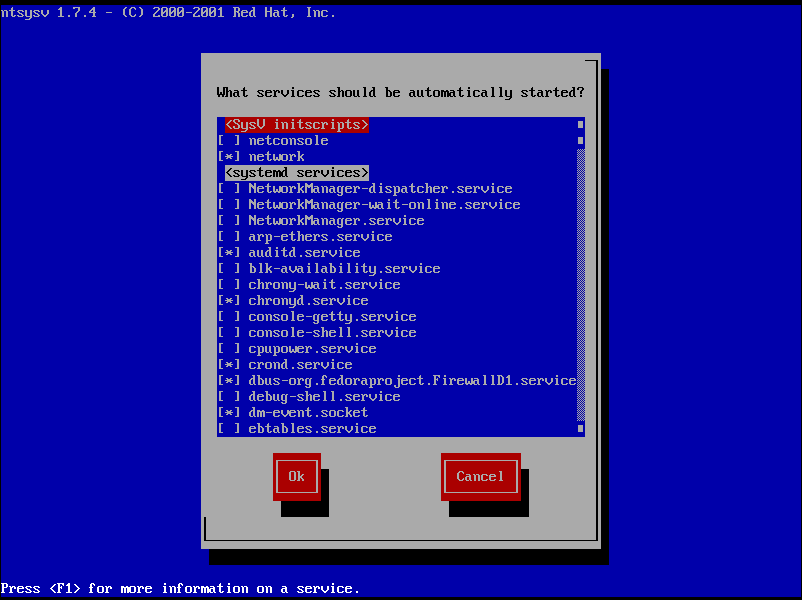
At the same time, to manage the services in the specified run level, not only the services in the current run level:
ntsysv –level 35
systemctl
systemctl is a controlling interface and inspection tool for the widely-adopted init system and service manager systemd.
- systemctl {option} name.servive
start: Start the service
stop: Stop the service
restart: Restart, stop first, then start the service
reload: reload the configuration file without completely stopping and starting the service
status: Status the service
is-active: Whether the startup was successful
is-failed: Whether the startup failed
enable: Auto-startup
disable: Turn off auto-startup
is-enabled: Whether to auto-startup
list-dependencies: View dependencies
mask: Block service
unmask: Unblock service
Example: systemctl start httpd.service
runlevel
A runlevel is a mode of operation in the computer operating systems that implement Unix System V-style initialization. Conventionally, seven runlevels exist, numbered from zero to six. S is sometimes used as a synonym for one of the levels. Only one runlevel is executed on startup; run levels are not executed one after another (i.e. only runlevel 2, 3, or 4 is executed, not more of them sequentially or in any other order).
runlevel
- Display the operating level of the system: runlevel
Switch multi-user mode
init 5
or
systemctl isolate multi-user.target