Critical Fortinet Flaw Exploited in “Connect:fun” Campaign
Forescout has detected a new campaign exploiting a vulnerability in Fortinet FortiClient EMS devices to disseminate malware.
The SQL injection vulnerability, CVE-2023-48788 (CVSS score: 9.8), enables unauthorized attackers to execute code through specially crafted queries without user interaction, making the attack relatively easy to implement.
Forescout is monitoring a campaign dubbed Connect:fun, named for its use of ScreenConnect and Powerfun programs post-compromise. The attack targeted an unnamed media company, whose vulnerable FortiClient EMS device was accessible online.
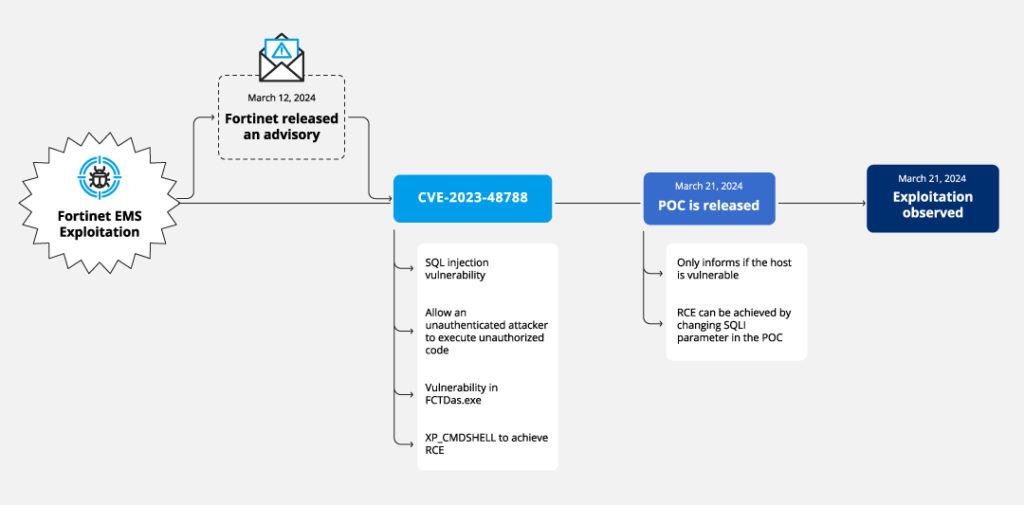
It is worth noting that on March 21, a proof-of-concept exploit for this vulnerability was published online. On March 25, this exploit was used to run PowerShell code, which downloaded the Metasploit Powerfun script and initiated a reverse connection to another IP address. It was also discovered that SQL queries were employed to download ScreenConnect from a remote domain using the certutil utility, after which the program was installed and established communication with a control server.
Forescout notes that the hackers, active at least since 2022, specialize in attacks on Fortinet devices and use infrastructure that incorporates both Vietnamese and German languages. The criminal activity indicates a manual component in the attacks, evidenced by numerous failed attempts to download and install software, as well as lengthy pauses between attempts. This confirms that the campaign is specialized, not part of a mass automated attack.
Companies are advised to install patches from Fortinet to neutralize threats, monitor suspicious traffic, and use firewalls to block potentially malicious requests.





