The hacker group UAC-0226 continues to aggressively evolve its malicious tool GIFTEDCROOK, which initially functioned as a browser data-stealing utility but has now acquired advanced capabilities, enabling the targeted exfiltration of confidential documents and files.
Researchers at Arctic Wolf reported that in June 2025, a wave of new campaigns utilizing the enhanced version of GIFTEDCROOK was detected. The malware is now capable of harvesting a wide array of files from infected devices, including documents, images, internal corporate materials, and browser data. Experts emphasize that the tool has transitioned into executing more sophisticated cyber-espionage operations, extracting intelligence from targeted systems with precision.
The earliest traces of this threat emerged in April 2025, when attackers distributed emails containing malicious Microsoft Excel documents embedded with harmful macros. Once activated, the macros would download and execute GIFTEDCROOK.
Initially, the malware focused on stealing browser cookies, history logs, and credentials from widely used web browsers such as Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Mozilla Firefox. However, as the campaign matured, its functionality expanded significantly.
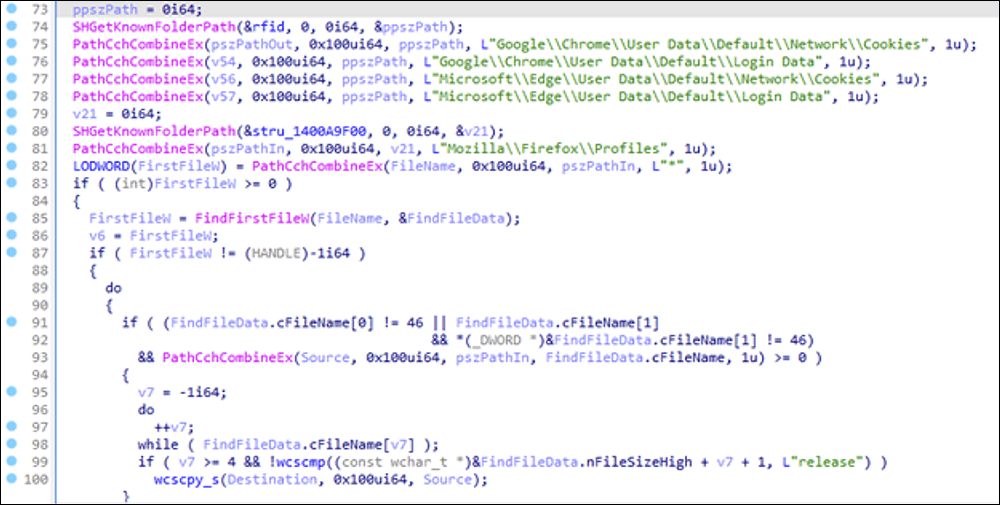
Versions 1.2 and 1.3, released after a trial edition in February 2025, introduced the ability to steal files up to 7MB in size, provided they were created or modified within the past 45 days. Targeted file types include text documents, spreadsheets, presentations, images, archives, emails, and VPN configuration files—specifically extensions such as .doc, .docx, .rtf, .pptx, .ppt, .csv, .xls, .xlsx, .jpeg, .jpg, .png, .pdf, .odt, .ods, .rar, .zip, .eml, .txt, .sqlite, and .ovpn.
To disseminate the malware, the attackers craft meticulously composed phishing emails containing seemingly legitimate PDF attachments. These messages include a link to a Mega cloud storage site hosting an XLSM document rigged with a malicious macro. When macros are enabled in Excel, the GIFTEDCROOK malware is silently deployed and executed.
Shortly after execution, the harvested data is compressed into a ZIP archive and exfiltrated via a Telegram channel under the attackers’ control. If the total size exceeds 20MB, the archive is automatically split into segments to facilitate undetected transfer over the network. Once exfiltration is complete, a cleanup script is triggered to erase all traces of the malware from the compromised device.
According to cybersecurity analysts, the latest iteration of GIFTEDCROOK is less concerned with harvesting credentials and more focused on the systematic collection of critical documents. Among the stolen data are PDFs, spreadsheets, text files, VPN configurations, and other internal resources—posing a significant threat to organizations handling sensitive information.
Furthermore, experts note that GIFTEDCROOK’s development mirrors broader trends in the threat landscape. While earlier versions were primarily credential-focused, the recent updates reflect a shift toward comprehensive espionage frameworks, designed to extract the maximum amount of intelligence from infected endpoints with surgical efficiency.