Vcurms RAT: New Attack Targets Java Systems
Fortinet’s FortiGuard Labs has unearthed a grave cyber threat dubbed Vcurms RAT, crafted by malefactors who employ email as a command-and-control center and utilize public services such as AWS and GitHub for harboring malicious code.
This campaign predominantly targets Java-installed platforms, posing a significant risk to any organization leveraging such systems. Successful deployment grants attackers comprehensive control over the breached networks.
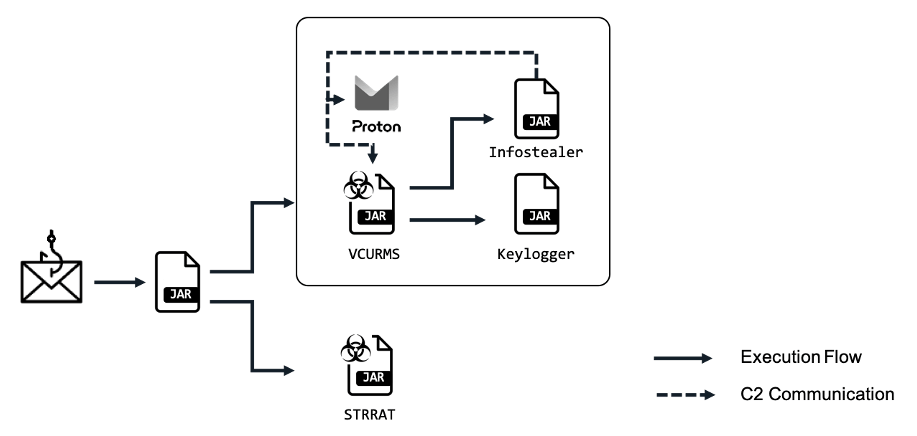
Users are compelled to download a malicious Java loader, serving as a conduit for disseminating Vcurms and the STRRAT trojan. These malicious emails are typically disguised as legitimate inquiries, coaxing recipients to verify payment information and download files hosted on AWS.
Attack flow
Once installed, the malware employs classic phishing techniques, including fake names and encrypted strings, to cloak its malevolent nature. Notably, the software utilizes the “DownloadAndExecuteJarFiles.class” class for downloading and executing additional JAR files, amplifying the malefactors’ capabilities.
The Vcurms component, functioning as a remote access trojan (RAT), connects with its command center via email, showcasing an elevated level of technical sophistication. It ensures persistence by replicating itself into the startup folder, identifying, and monitoring victims through keylogging and password recovery functions.
Furthermore, the malware leverages advanced obfuscation tools, such as the Branchlock obfuscator, to evade detection and analysis. Despite the challenges, researchers persist in developing deobfuscation methods and unraveling the workings of Vcurms.
Vcurms shares similarities with the Rude Stealer malware but distinguishes itself with unique information transmission methods. Its primary objective is to extract confidential data from widely used browsers including Chrome, Brave, Edge, Vivaldi, Opera, OperaGX, and Firefox, and applications like Discord and Steam.
In response to the Vcurms threat, FortiGuard Labs recommends adopting a series of preventative measures in its blog. Primarily, it’s crucial to deploy updated cybersecurity solutions and perform network segmentation. Additionally, adhering to proper password management practices and exercising caution with email attachments are paramount to reducing infection risks.