slither: Static Analyzer for Solidity
Slither, the Solidity source analyzer
Slither is a Solidity static analysis framework written in Python 3. It runs a suite of vulnerability detectors, prints visual information about contract details, and provides an API to easily write custom analyses. Slither enables developers to find vulnerabilities, enhance their code comprehension, and quickly prototype custom analyses.
Features
- Detects vulnerable Solidity code with low false positives
- Identifies where the error condition occurs in the source code
- Easy integration into continuous integration and Truffle builds
- Built-in ‘printers’ quickly report crucial contract information
- Detector API to write custom analyses in Python
- Ability to analyze contracts written with Solidity >= 0.4
- Intermediate representation (SlithIR) enables simple, high-precision analyses
Install
Slither requires Python 3.6+ and solc, the Solidity compiler.
Using Pip
$ pip install slither-analyzer
Using Git
$ git clone https://github.com/trailofbits/slither.git && cd slither
$ python setup.py install
Use
Run Slither on a Truffle application:
slither .
Run Slither on a single file:
Slither can be run on:
- A
.solfile - A Truffle directory
- A directory containing
*.solfiles (all the*.solfiles will be analyzed) - A glob (be sure to quote the argument when using a glob)
Configuration
--solc SOLC: Path tosolc(default ‘solc’)--solc-args SOLC_ARGS: Add custom solc arguments.SOLC_ARGScan contain multiple arguments--disable-solc-warnings: Do not print solc warnings--solc-ast: Use the solc AST file as input (solc file.sol --ast-json > file.ast.json)--json FILE: Export results as JSON
Detectors
By default, all the detectors are run.
| Num | Detector | What it Detects | Impact | Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | suicidal |
Functions allowing anyone to destruct the contract | High | High |
| 2 | uninitialized-local |
Uninitialized local variables | High | High |
| 3 | uninitialized-state |
Uninitialized state variables | High | High |
| 4 | uninitialized-storage |
Uninitialized storage variables | High | High |
| 5 | arbitrary-send |
Functions that send ether to arbitrary destinations | High | Medium |
| 6 | controlled-delegatecall |
Controlled delegatecall destination | High | Medium |
| 7 | reentrancy |
Reentrancy vulnerabilities | High | Medium |
| 8 | locked-ether |
Contracts that lock ether | Medium | High |
| 9 | const-func |
Constant functions changing the state | Medium | Medium |
| 10 | tx-origin |
Dangerous usage of tx.origin |
Medium | Medium |
| 11 | assembly |
Assembly usage | Informational | High |
| 12 | constable-states |
State variables that could be declared constant | Informational | High |
| 13 | external-function |
Public function that could be declared as external | Informational | High |
| 14 | low-level-calls |
Low level calls | Informational | High |
| 15 | naming-convention |
Conformance to Solidity naming conventions | Informational | High |
| 16 | pragma |
If different pragma directives are used | Informational | High |
| 17 | solc-version |
Old versions of Solidity (< 0.4.23) | Informational | High |
| 18 | unused-state |
Unused state variables |
Printers
To run a printer, use –print and a comma-separated list of printers.
| Num | Printer | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | call-graph |
Export the call-graph of the contracts to a dot file |
| 2 | contract-summary |
Print a summary of the contracts |
| 3 | function-summary |
Print a summary of the functions |
| 4 | human-summary |
Print a human-readable summary of the contracts |
| 5 | inheritance |
Print the inheritance relations between contracts |
| 6 | inheritance-graph |
Export the inheritance graph of each contract to a dot file |
| 7 | slithir |
Print the slithIR representation of the functions |
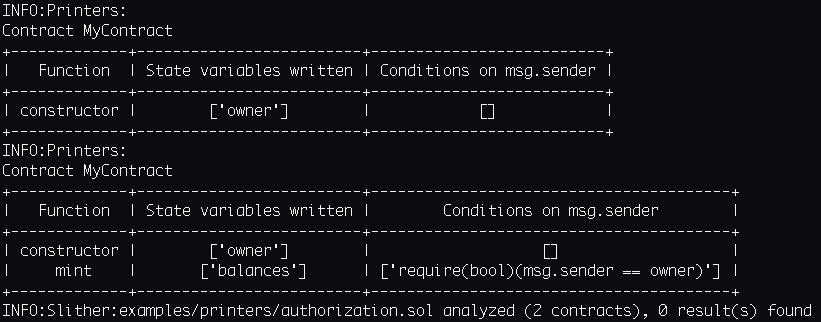
| 8 | vars-and-auth |
Print the state variables written and the authorization of the functions |
Tutorial
Copyright (C) 2018





