Pegasus Malware – The Most Powerful Spyware Programs
Pegasus is considered one of the most powerful spyware programs available today, with a far more comprehensive data-stealing capability than other spyware programs, including the ability to collect information on everything from high-value data such as passwords and contact information to data from other applications. In this article, the author will provide an overview of the Pegasus malware and the Chrysaor variant, as well as the attack methods and how to protect yourself from this dangerous malware.
Overview
Pegasus is a spyware program developed by the NSO Group (Israel), which can be installed secretly on mobile phones or other devices running the iOS and Android operating systems (another version of Pegasus is Chrysaor). According to the latest report on Pegasus, the malware can exploit most versions of iOS.
NSO is an Israeli technology company responsible for collecting intelligence on criminals and terrorists. The company developed the Pegasus spyware program for the iOS operating system to combat cybercrime and track terrorists. However, Pegasus was later purchased or ordered by some governments to collect intelligence, tracking journalists, opposition politicians, and dissidents, or more broadly, tracking the behavior of all users on their smartphones.
Pegasus has an extensible and modular library of audio and messaging interception capabilities, with the libaudio.dylib library for audio and libimo.dylib for messaging is the most common, but there are also specialized libraries for individual applications such as WhatsApp and Viber. Additionally, Pegasus has an impressive self-concealing capability. The spyware will self-destruct if it cannot communicate with the command and control (C&C) server for 60 days or if it detects that it has been installed on the wrong device with the SIM card that it was “registered” to.
THE SCOPE OF IMPACT OF THE PEGASUS MALWARE
Pegasus is a highly sophisticated, comprehensive spyware program that exploits zero-day vulnerabilities. As a result, the price of this malware is relatively high. For this reason, the target, victims of this malware are people with high social status, wealth, and assets, such as Royal families, Businessmen, Key members of government, Journalists, dissidents, Political opponents
Nations and governments purchase or order this spyware for tracking and monitoring journalists, human rights activists, and their political opponents. Figure 1 shows the density of countries using Pegasus software that has been previously released.
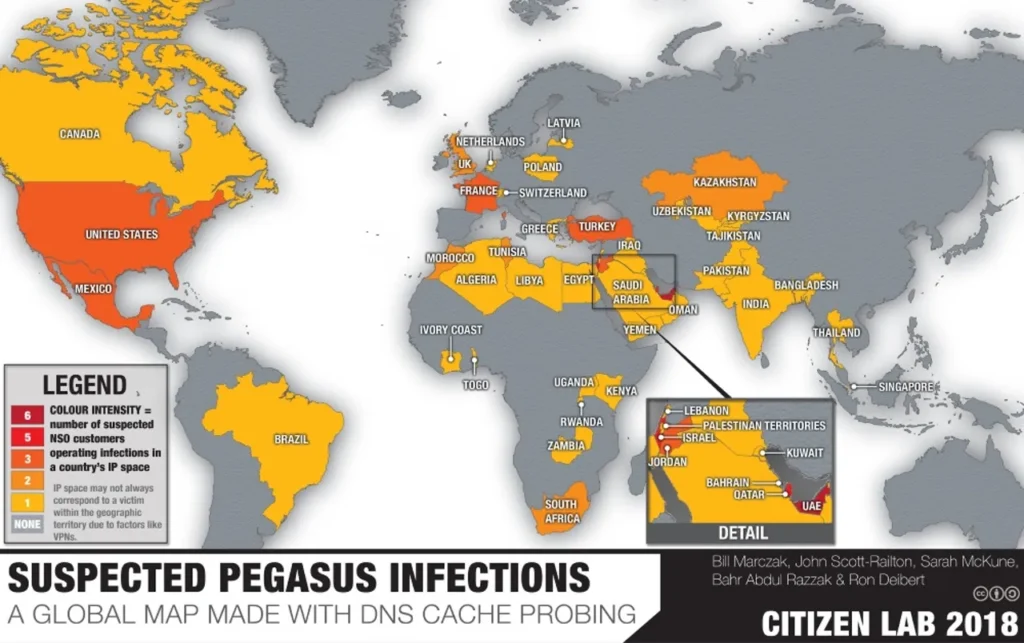
Image: Citizen Lab
CHRYSAOR MALWARE
Chrysaor is a modified version of the Pegasus malware, which is one of the most dangerous spyware programs designed to target Android devices. So far, Chrysaor is known to have infected primarily some Android devices in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Israel, Georgia, Mexico, and Turkey.
When Chrysaor takes control, it will collect call log data from WhatsApp, Facebook, Twitter, Skype, and Gmail apps. The software will also access the camera and microphone, take screenshots, and act as a keylogger by recording keystrokes. Chrysaor also can self-delete from the compromised system if it detects that the user is accessing it and is investigating suspicious activity taking place on their device.
Recently, Google researchers have found a vulnerability in the Android operating system that allows attackers to have full access to at least 18 smartphone models, including Pixel, Xiaomi, Huawei, Motorola, Oppo, Samsung, etc. Android devices can be attacked and infected by Chrysaor even without exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities using a technique called Frameroot.
After Chrysaor is installed, attackers can survey the victim’s activities on the device and the surrounding area, taking advantage of the microphone, and camera, collecting data, logging, and tracking activities on communication applications such as phone and SMS. A sample Chrysaor application has been analyzed and shows the ability to be adapted to devices running Jellybean (4.3) or older versions. The application uses 06 techniques to collect user data as follows:
- Repeated commands: Uses alarms to periodically repeat actions on the device to steal information, including collecting location data.
- Data collector: Renders all existing content on the device into a queue. The data collector is used in conjunction with repeating commands to collect user data, including SMS settings, SMS messages, call logs, browser history, contacts, email, and messages from messaging applications, including WhatsApp, Twitter, Facebook, Kakao, Viber, and Skype.
- ContentObservers: Uses the Android ContentObserver framework to collect changes in SMS, calendar, contacts, mobile information, email, WhatsApp, Facebook, Twitter, Kakao, Viber, and Skype.
- Takes a screenshot of the current screen through the raw frame buffer.
- Keylogging: Record input events by hooking IPCThreadState::Transact from /system/lib/libbinder.so, and intercepting android::parcel with the interfacecom.android.internal.view.IInputContext.
- RoomTap: Silently answers phone calls and connects in the background, allowing the caller to hear conversations within the range of the phone’s microphone. If the user unlocks the device, they will see a black screen while the application terminates the call, resets the call settings, and prepares the user to interact with the device normally.
Attack Techniques and Detection and Prevention Methods
Attack Techniques
The previous version of the Pegasus spyware, released in 2016, could attack phones using the “spear[1]phishing” technique, which involves sending text messages or emails containing malicious links to the target. However, access would depend on whether the target clicks on this link.
In 2019, Pegasus released a version that could attack phones using the “zero-click” method, meaning that users could be attacked even if they did not perform any actions. Pegasus also allows it to infiltrate mobile devices through missed calls on WhatsApp and can even delete the call history, making users unaware that they are being targeted.
Detection Methods
Several different methods can be used to assist in the investigation and identification of devices that have been attacked by Pegasus. These detection methods are drawn from the analysis of devices from victims who have been attacked and include:
- Receiving Pegasus messages with strange links.
- The appearance of malicious processes on the device.
- Analyzing the Safari web browsing history, from which to detect redirects that have been performed and malicious queries.
- Searching iMessage with suspicious iCloud accounts.
- Using mobile verification tools to help find traces of Pegasus attacks on the device.
Prevention Techniques
We can completely proactively limit and effectively prevent attacks by:
- Updating all applications and systems as soon as the publisher provides new updates.
- Do not install applications from any website other than the AppStore, or Google Play, especially from unofficial websites.
- Do not use jailbreak software.
- When accessing public networks, you should use your own VPN.
- Do not bring your phone when attending sensitive meetings.
- Do not click on strange links sent from unknown addresses.
Conclusion
With its superior features, the Pegasus malware and its variant, Chrysaor, are a threat not only to citizens but also to national security, as politicians are the targets of this malware. Therefore, detection and prevention measures are essential to protect users’ devices from the increasingly sophisticated cyber threat landscape.





