Linux system information and running status monitoring
In the file system of Linux, there is a special directory “/proc”. Many interesting things can be found in this directory, such as
- /proc/cpuinfo //Information about the local CPU
- /proc/meminfo //Usage information of local memory and swap partition
- /proc/modules// Information about the hardware modules installed on the machine
-
/proc/mounts //Device information on the mounted mount
 For example, enter the subdirectory named “1”:
For example, enter the subdirectory named “1”:cd /proc/1
df command

Used to view the status information of the Linux file system, and display the capacity, used, unused, and mount points of each partition. Such as:
-
- df -k //Display information for each partition in kilobytes (KB)
- df -a //Display all partitions, including partitions of size 0
- df -T //Displays the partition type (EXT2 or EXT3, etc.)
du command
- Lets you view the size of a file or folder. Such as:
- du -b /home //Show the size of each subfolder under the “/ home” folder in bytes
- du -ks home //Display the total size of the “/home” folder in kilobytes (KB)
top command
Used to view system status information in real-time. After running this command, the following information will be displayed on the screen: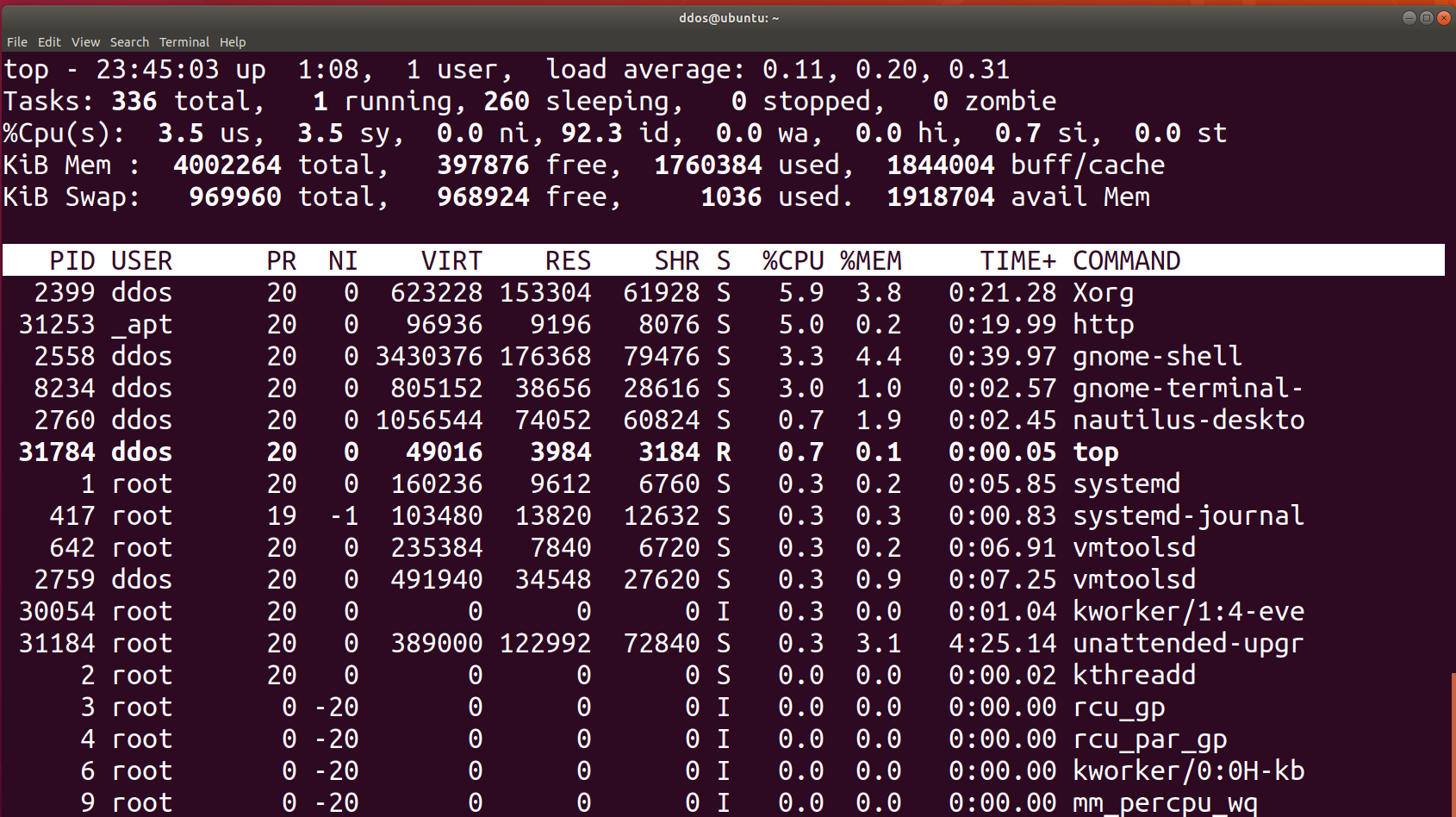
-
- CPU states: including user process occupancy rate, system process occupancy rate, user priority process occupancy rate, and idle CPU resource rate
- Memory status (Mem): including total memory, usage, free capacity, etc
- Swap status: Includes the total amount of swap partitions, usage, and free capacity
- Status of each process: including process ID, user name, priority, CPU and memory usage, and the command line executed when the process was run






