Lazarus Group Strikes Again: Job Lure Deploys Kaolin RAT
The Lazarus Group, a notorious hacking collective traditionally associated with North Korea, utilized enticing job offers to deliver a new Remote Access Trojan (RAT) known as Kaolin RAT during attacks targeting individuals in Asia in the summer of 2023.
As reported by Luigino Camastra, a security researcher from Avast, this malicious software possesses capabilities beyond those of a standard RAT, including modifying the timestamp of the last entry of a selected file and downloading any DLL binary file from the attackers’ C2 server.
The RAT serves as a conduit for the delivery of the FudModule rootkit, which recently exploited a vulnerability in the appid.sys driver (CVE-2024-21338, CVSS score: 7.8) to obtain read/write primitives in the kernel and ultimately disable security mechanisms.
The use of job offer lures by Lazarus to infiltrate systems is not new. The long-term campaign named “Operation Dream Job” demonstrates that the group uses various social networks and instant messaging platforms to deliver malware.
The infection chain begins when the targets execute a malicious optical disk image (ISO) containing three files, one of which masquerades as an Amazon VNC client (“AmazonVNC.exe”), which is a renamed version of the legitimate Windows application “choice.exe”.
The other two files, “version.dll” and “aws.cfg”, act as catalysts for the initiation of the infection. Specifically, the executable “AmazonVNC.exe” is used for DLL Sideloading of the malicious library “version.dll”, which in turn launches the IExpress.exe process and injects into it the payload contained in “aws.cfg”.
This payload is designed to download shellcode from a C2 domain (“henraux[.]com”), which is purportedly owned by an Italian company specializing in the quarrying and processing of marble and granite. It is likely that this domain was compromised by the attackers.
The shellcode is used to initiate RollFling, a DLL-based loader that serves to obtain and execute the next stage of malware known as RollSling, which was disclosed by Microsoft last year.
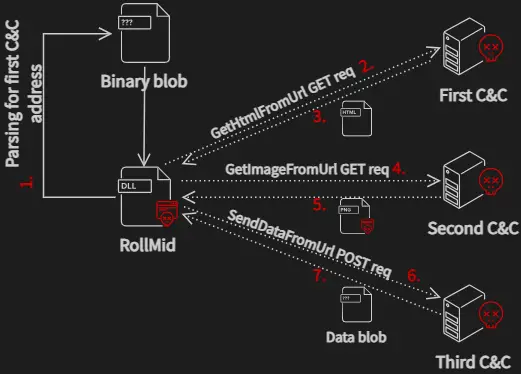
RollSling, executed directly in memory in an attempt to evade detection by antivirus software, represents the next stage of the infection process. Its primary function is to initiate the execution of a third loader called RollMid, which also runs directly in memory.
RollMid possesses capabilities that prepare the ground for further attacks and establish communication with a C2 server, including a three-step process in which the malware:
- Connects to a first C2 server to retrieve an HTML file containing the address of a second C2 server,
- Connects to the second C2 server to obtain a PNG image embedded with a malicious component using steganography,
- Transmits data to a third C2 server using the address specified in the hidden data within the image,
- Extracts additional data encoded in Base64 from the third C2 server, which constitutes the Kaolin RAT.
Amid these events, Luigino Camastra noted that Lazarus targeted individuals through fake job offers and utilized a sophisticated set of tools and malicious actions to achieve enhanced persistence, circumventing protective measures in victim systems.





