GearGoat : Car Vulnerabilities Simulator
GearGoat: Car Vulnerabilities Simulator
A Python implementation inspired by ICSim. Currently supports running on a single interface “vcan0” and fixed arbitration IDs for the actions including, turn indicators, door lock unlock indicators, and speedometer.
The simulator runs in a browser with control buttons for the user to interact.
Prerequisites
- Linux machine
- Docker (for installing docker on Linux)
sudo sh get-docker.sh
Further instructions here
Installation
Step 1. Clone the repo and navigate into the directory
git clone https://github.com/ine-labs/GearGoat.git
cd GearGoat
Step 2. Inside the repository directory, run the following to install the required utilities and build the docker container.
sudo chmod +x initial_setup.sh
sudo ./initial_setup.sh
Step 3. Setup the vcan0 interface
sudo chmod +x vcan_setup.sh
sudo ./vcan_setup.sh
sudo apt-get install -y linux-modules-extra-$(uname -r)
sudo docker run –network=“host“ –privileged geargoat
ip_address=$(hostname -I | awk ‘{print $1}’)
url=”http://$ip_address”
echo $url
Usage
There are mainly three car actions that can be performed with this web UI, which includes:
- Toggling turn signals
- Locking/Unlocking Doors
- Updating the speedometer.
Try out each button and observe the actions in the UI.
Clicking on indicator buttons switches the state for a fraction of a second. The color changes to “orange”. Click for a slightly longer duration to register the signal change.
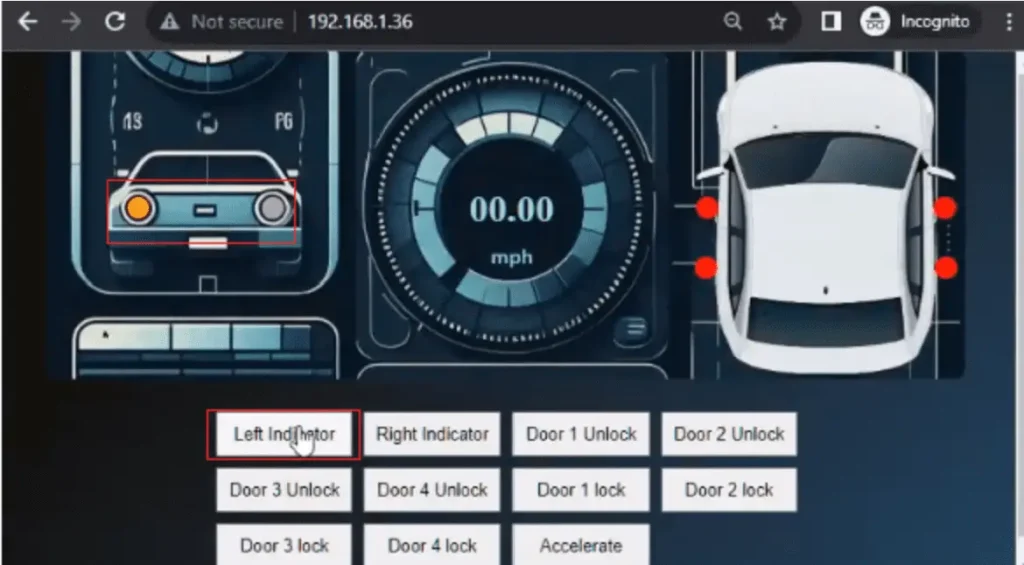
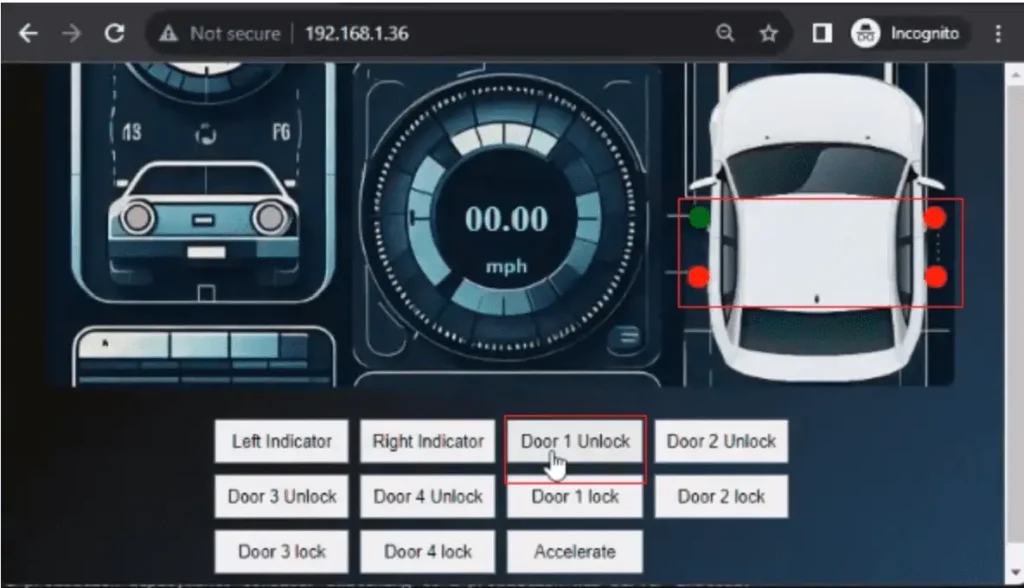
The door is initially locked indicated by “red”. It can be unlocked by clicking the corresponding door unlock button which turns the indicator to “green”. Clicking the corresponding door lock button again will revert it to “red”.
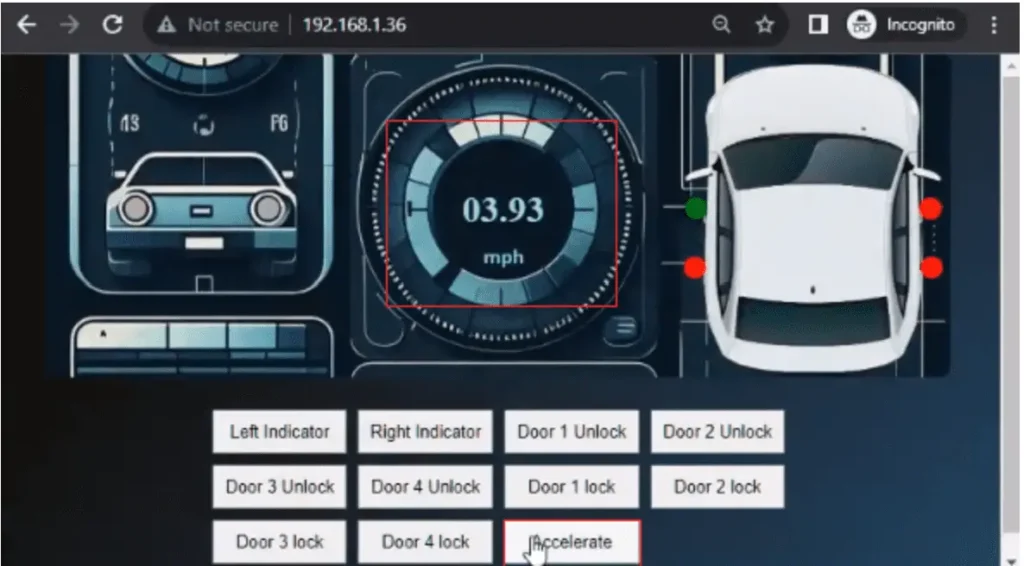
Finally, the accelerate button will respond to mouse clicks. Clicking and holding the button (mousedown) will result in a speed increase and releasing the button(mouseup) results in speed falling.
All these actions generate corresponding CAN packets.
After usage, you can turn off the simulator by:
CONTAINER_ID=$(sudo docker ps -qf “ancestor=geargoat“)
sudo docker stop $CONTAINER_ID
Tutorial
Copyright (C) 2024 Pranjal Soni, Software Engineer (Cloud), INE psoni@ine.com (Primary Contributor), Nishant Sharma, Director (Lab Platform), INE nsharma@ine.com (Guidance), Sanjeev Mahunta, Software Engineer (Cloud), INE smahunta@ine.com





