Fortinet Vulnerability Exploited: Patch Now! PoC Published
Security researchers at Horizon3 have disclosed a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit for a critical vulnerability in Fortinet’s FortiClient EMS, which is currently being actively exploited by hackers.
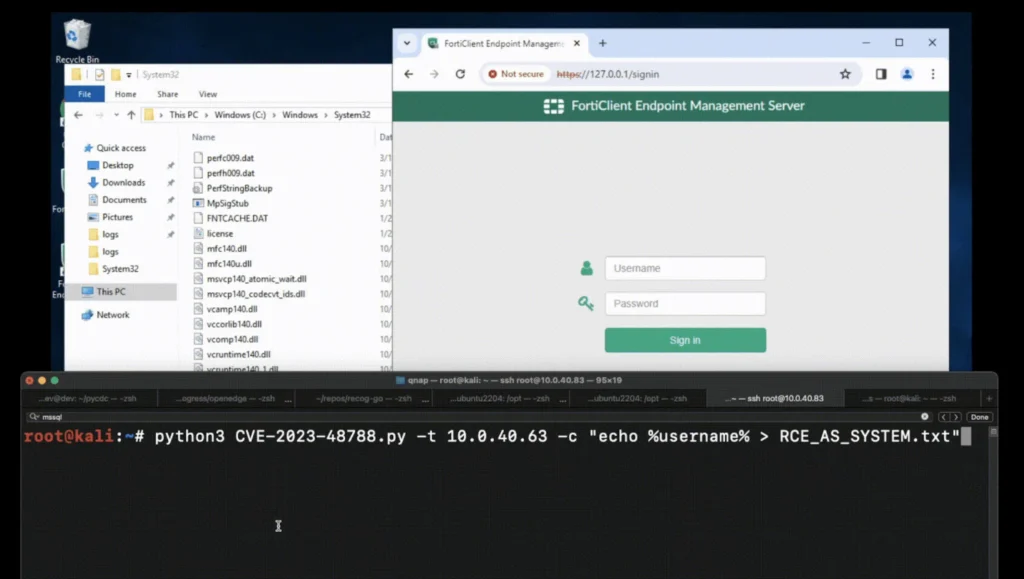
The SQL injection vulnerability, CVE-2023-48788 (with a CVSS score of 9.8), is found within the DB2 Administration Server (DAS) component and affects FortiClient EMS versions 7.0 (from 7.0.1 to 7.0.10) and 7.2 (from 7.2.0 to 7.2.2), allowing an unauthenticated attacker to perform remote code execution (RCE) with SYSTEM privileges without user interaction.
Initially, Fortinet did not report whether evidence of the vulnerability’s exploitation in attacks was discovered, but in their latest security bulletin, the company clarified that the vulnerability is being exploited in the wild.
A week after Fortinet released fixes, the security research team at Horizon3 published a technical analysis and shared a PoC exploit that validates the vulnerability without facilitating remote code execution.
For the PoC exploit to be used in RCE attacks, it needs to be modified to utilize the xp_cmdshell procedure in Microsoft SQL Server to create a Windows command shell to execute code.
Shodan and Shadowserver services report over 440 and 300 FortiClient EMS servers accessible online, respectively, with the majority located in the USA.
It’s important to note that vulnerabilities in Fortinet products are often exploited for unauthorized access to corporate networks to conduct ransomware attacks and cyber espionage, including the use of zero-day exploits.





