Critical Microsoft Exchange Flaw: 97,000 Servers at Risk
Up to 97,000 Exchange servers may be susceptible to a critical vulnerability designated as CVE-2024-21410, a subject we broached several days ago. This flaw permits unauthenticated remote attackers to execute NTLM Relay attacks on Microsoft Exchange servers and escalate their privileges within the system. Exchange Server is extensively utilized in business environments to facilitate communication and collaboration among users, offering services such as email, calendars, contact management, and task organization.
Microsoft rectified the aforementioned vulnerability on February 13, at a time when it was already being exploited as a zero-day. Yesterday, on February 19, the threat monitoring service Shadowserver announced that its scanners had detected approximately 97,000 potentially vulnerable servers. Of these, 68,500 might be vulnerable depending on whether administrators have implemented mitigation measures, while specifically 28,500 servers are susceptible to direct exploitation of CVE-2024-21410.
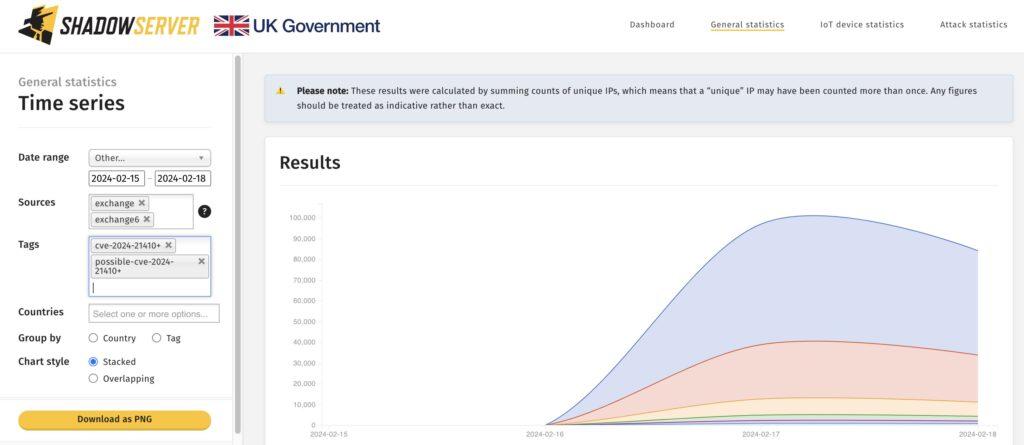
The countries most significantly impacted by potential hacker attacks include:
- Germany — 22,903 servers;
- United States — 19,434 servers;
- United Kingdom — 3,665 servers;
- France — 3,074 servers;
- Austria — 2,987 servers;
- Russia — 2,771 servers;
- Canada — 2,554 servers;
- Switzerland — 2,119 servers.
Currently, there is no publicly available Proof of Concept (PoC) exploit for CVE-2024-21410, which somewhat limits the number of attackers exploiting this vulnerability.
To address CVE-2024-21410, system administrators are advised to apply the Cumulative Update 14 (CU14) for Exchange Server 2019, released as part of the latest Patch Tuesday update, which includes protection against NTLM credential theft.
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) of the United States has also added CVE-2024-21410 to its catalog of “Known Exploited Vulnerabilities” (KEV), granting federal agencies until March 7, 2024, to apply the available updates, implement mitigating measures, or cease using the product altogether.
The exploitation of CVE-2024-21410 could have grave repercussions for organizations, as attackers with elevated privileges on the Exchange server could gain access to sensitive information, such as emails, and utilize the server as a springboard for further attacks on the network.
Should your organization employ an Exchange Server, it is imperative not to delay the update; the emergence of a publicly accessible PoC would significantly exacerbate the current situation.