China’s Cyber Espionage Escalates with DOPLUGS Malware
In a recent report by Trend Micro, it was revealed that the Chinese cyber espionage group Mustang Panda has intensified its operations across Asia, employing a modified variant of the PlugX malware named DOPLUGS. This updated version boasts unique functionalities designed primarily for the delivery of the main malicious payload.
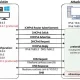
The primary targets of these assaults have been Taiwan and Vietnam, with Hong Kong, India, Japan, Malaysia, Mongolia, and China also being affected to a lesser extent. The infection chain is initiated through the dissemination of phishing messages, which serve as the conduit for the delivery of the initial stage payload. This payload, while displaying a counterfeit document on the victim’s screen, clandestinely unpacks a digitally signed executable file vulnerable to DLL Sideloading. This process is employed to load a malicious DLL library that initiates PlugX.

Subsequently, the PlugX malware facilitates the delivery of a Remote Access Trojan (RAT), such as Poison Ivy or Cobalt Strike Beacon, establishing a connection with the Command and Control (C2) server.
DOPLUGS functions as a loader with four management commands, one of which is dedicated to downloading the standard version of the PlugX virus. Trend Micro has also identified DOPLUGS samples integrated with the KillSomeOne module, responsible for the dissemination of malware, information gathering, and theft of documents from USB drives.
PlugX malware, also known as Korplug, is a modular implant installed post-exploit, renowned for its array of capabilities including data exfiltration and the utilization of compromised machines for malicious purposes.
One of the key tactics employed by PlugX is the DLL Sideloading technique, which involves the loading of a malicious DLL library from a digitally signed software application. A valid digital signature can mislead certain security tools, allowing hackers to remain undetected, maintain persistence, escalate privileges, and circumvent file execution restrictions.