Palo Alto Networks’ Unit 42 reports that the cybercriminal group Muddled Libra is actively targeting cloud applications and cloud service providers in a bid to steal confidential data.
According to the report, the attackers are focused on extracting data from SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) applications and CSP (Cloud Service Provider) services, using this information for further attacks and extortion. Notably, Muddled Libra employs sophisticated social engineering techniques for initial penetration into the target networks.
Muddled Libra is known for its skill in evading detection by employing techniques that allow it to operate stealthily and modify its command and control methods to adapt to various victim networks. Their operations include extortion and data theft.

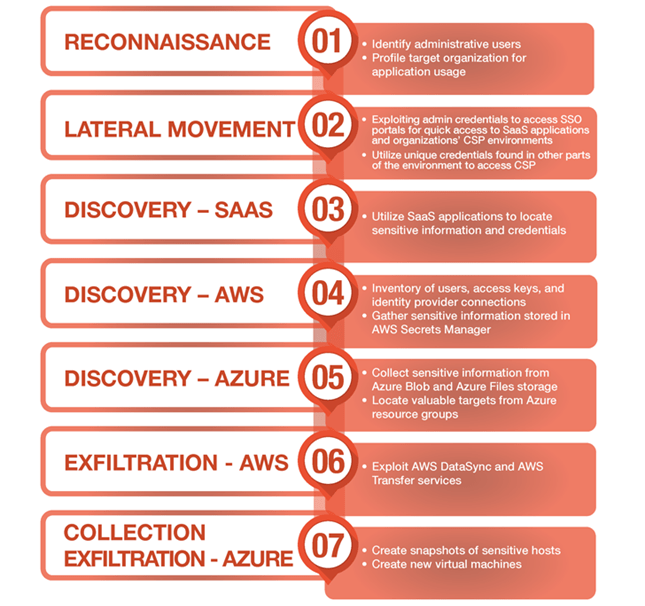
A distinctive feature of Muddled Libra’s tactics includes reconnaissance aimed at identifying administrative users to subsequently acquire their passwords under the guise of technical support. The group also conducts an in-depth analysis of the applications and cloud services used by organizations.
Last year, from late July to early August 2023, Muddled Libra successfully circumvented IAM (Identity and Access Management) restrictions by exploiting the Okta service to access SaaS applications and the cloud infrastructure of various organizations.
Additionally, if the victim’s cloud platform does not support SSO (single sign-on) integration, the hackers conduct extensive searches to uncover CSP credentials, often stored in unprotected locations.
The objective of their data collection efforts is specifically to gain access to services such as AWS IAM, Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), AWS Secrets Manager, as well as access keys to Azure storage solutions.
Exploiting CSP services and features, including AWS DataSync and AWS Transfer tools, as well as the technique of creating disk snapshots for transferring data from Azure environments, enables Muddled Libra to effectively gather data.
Palo Alto Networks advises organizations to implement additional authentication measures, including the use of hardware tokens or biometrics.