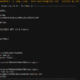
AMD EPYC Genoa Pictured
AMD released its EPYC 7004 server processor codenamed Genoa recently. Compared with the previous generation products, the number of CCDs packaged inside the new processor has increased from 8 to 12, the maximum number of cores has increased from 64 to 96 cores, and supports 12-channel DDR5 memory, providing 128 PCI-E 5.0 channels. At the press conference, AMD also showed what the processor looked like after it was opened.

It can be seen that CCDs are still arranged around a huge IOD in the EPYC Genoa processor, but the number of CCDs has increased to 12, and each CCD has 8 Zen 4 cores, so the total number of cores has reached 96. Like the consumer-grade Ryzen 7000 processor, AMD has gold-plated the CCD and IOD surfaces, which increases thermal conductivity and allows the temperature inside the core to dissipate as quickly as possible. AMD only showed 12 CCD models at the scene, in fact, it has 8 CCDs and 4 CCDs.

The size of this huge IOD on EPYC Genoa is 16.07*26.08mm and the area is 419.1mm2, while the IOD on Ryzen 7000 is only 122mm2. Compared with consumer-grade processors, the IOD area of server processors has increased by about 3.5 times. The main reason is naturally that it has to be connected to 12 CCDs, and it also supports 12 channels of memory and 128 PCI-E 5.0 channels. Like consumer processors, this IOD is also produced using TSMC’s 6nm process.
The EPYC 7004 server processor uses an SP5 socket and can be equipped with up to 12 CCDs, each CCD has 8 Zen 4 architecture cores, and the L3 cache is 32MB, each core has 1MB of L2 cache, adding up to a total of 96 cores with 192 threads, 96MB of L2 cache and 384MB of L3 cache, supporting AVX-512 and VNNI instructions; it also implements support for CXL 1.1+, providing breakthrough memory expansion capabilities.
Via: wccftech